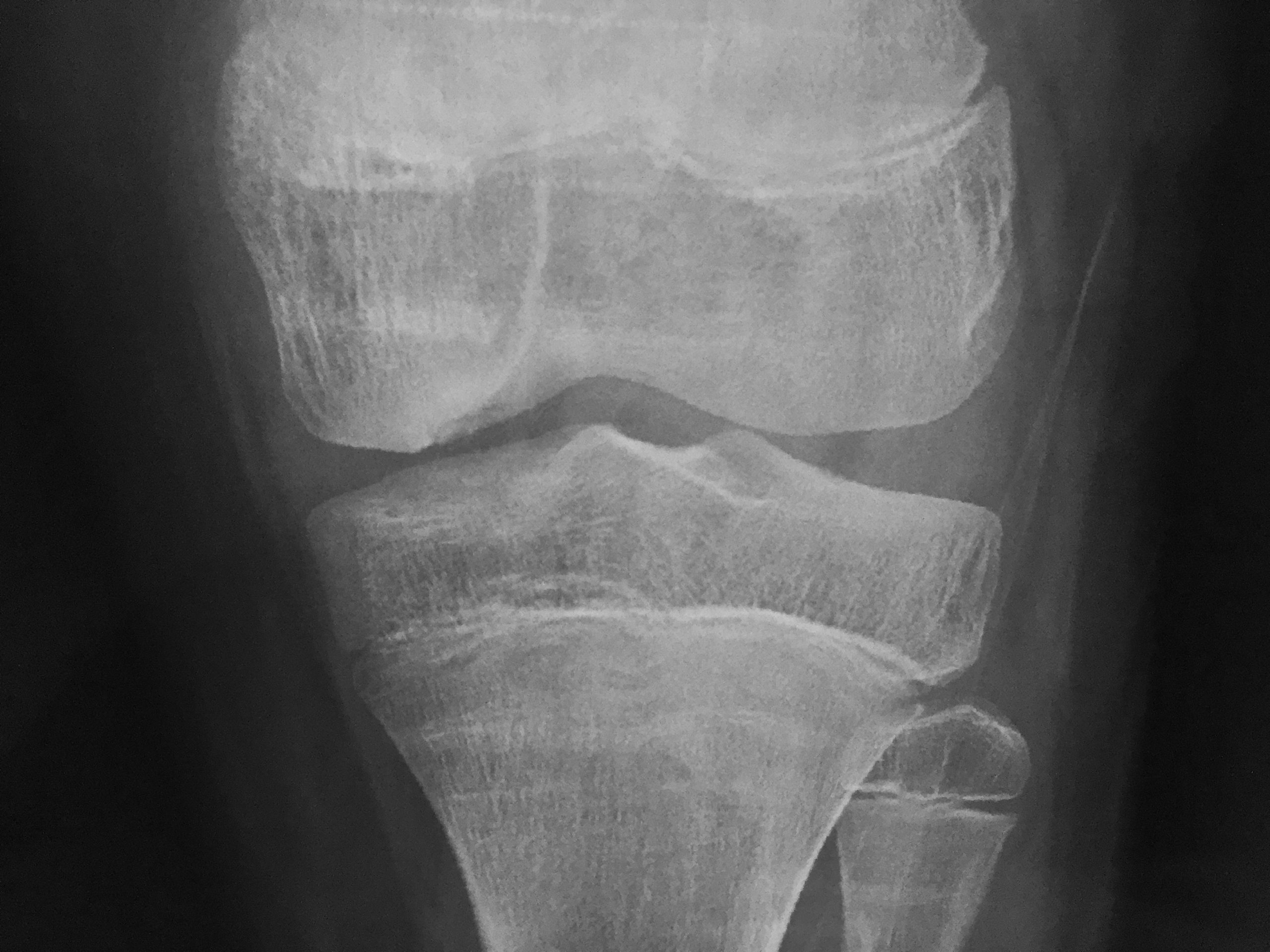
OCD (Osteochondritis dissecans) of knee
Normal joint cartilage is important for having a joint that bends smoothly. The normal cartilage is smooth and slippery and firmly attached to underlying subchondralbone. When the cartilage is damaged, it will not repair itself.
Osteochondritis dissecans, often called OCD is a pathologic condition that causes loosening of cartilage from its supporting bone. OCD most often occurs in the knee joint (medial femoral condyle), although it can also occur in other joints like ankle and the elbow. Mostly it is adult disease but It can occur in adolescent(open physis) also.
The cause of OCD is not well understood. In OCD, The blood flow to the subchondral bone around a joint cartilage decrease so there is softening of the overlying articular cartilage with intact articular surface in early stage than it leads to early articular cartilage separation. After some time this early cartilage separation become partial detachment of lesion and lastly there is osteochondral fragment float in knee and becomes loose body.
Reason for this disruption of blood flow, is thought to be related to repetitive stress or even traumatic injury to the bone. As the blood flow to the bone is diminished, the attached cartilage can separate away from the bone.
Symptoms (What you feel)
You feel pain which is activity related and poorly localised.
You may feel recurrent swelling (effusion) of knee joint.
You feel mechanical symptoms (locking) or instability of knee joint but when it is present then it indicates that you have advanced disease.
Diagnosis
Physical examination (what your doctor feel)
your doctor will check your knee for swelling and tenderness — comparing your injured knee to your normal knee. He may also move your knee into a variety of positions to assess range of motion and overall function of the joint and to do some specific test for various disease.
Your doctor may feel localised tenderness, and or stiffness and or swelling and or some specific test positive (wilson test).
Often the diagnosis of (Osteochondritis dissecans) OCD cannot be confirmed on the basis of physical examination alone, so you may need investigations to confirm the disease and rule out other causes and to determine the severity of the injury. These investigations may include:
X-ray – Most of OCD lesion will show up on x-ray. Your doctor may need specific x-ray view (tunnel or notch view) to clear show up these lesion.
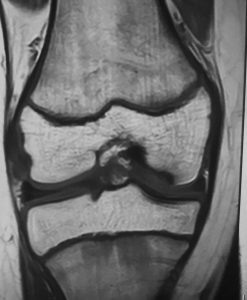
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – MRI is very useful to see exact site and size of lesion. MRI will show status of subchondral bone and cartilage and clearly show up stage of disease. Loose bodies in OCD are osteochondral so it may not show up in X-ray so MRI is necessary for diagnosis and for planning of treatment of disease.
Treatment
There are a number of factors that must be considered when determining treatment for OCD.many cases of OCD can be heal completely with conservative treatment.
Patient Age is the most important prognostic factor for OCD. Patients who have open growth plates (children and adolescents) have a much better prognosis to heal an OCD with both surgical and non-surgical treatments.
Size and Location decide nonsurgical or surgical treatment. Larger fragments and fragments in more critical parts of the joint are generally treated more aggressively with surgery.
Degree of Fragmentation/Detachment OCD fragments are also decide surgical or nonsurgical treatment. Unstable fragments that are more susceptible to this separation are most often surgically repaired. 50 to 75% of stable fragments are more likely to heal with nonsurgical treatment.
Nonsurgical treatment
Depending on the combination of factors, your orthopaedic surgeon can make a recommendation for nonsurgical treatment. When an OCD fragment is likely to heal, non-surgical treatment can be effective.
Nonsurgical treatment of OCD can take from 12 to 18 months. During that time, it is important that you have to stop doing everything that causes pain to the knee. It means you should avoid exercise and sports. You may require using crutches or wearing a brace for a couple of months when symptoms are present. As knee symptoms ease, exercises can be started that don’t cause weight through your foot. The exercises should be done carefully and should not cause any pain.
Surgical treatment
The goal of surgical treatment is to give a stable cartilage surface of the joint. If lesion is partially detached and it is thought that the fragment can heal, your doctor will most likely try to repair the OCD lesion.
Repair usually by using headless screws or pins to hold the fragment in place. We mostly use pins that are made of bioabsorbable material (rather than metal) so that they will not cause future problems to the joint cartilage.Other options for repair of lesion is subchondral retrograde drilling.
If the potential of healing is low, then loose osteocartilage fragments will be removed from the knee, and treatment will be focused on stimulating new cartilage growth in the void on the joint surface.
Methods of Stimulating New Cartilage Growth
- Micro-fracture- Asurgery is performed to stimulate blood flow to the area of damage, which can allow cartilage healing.
- OATS/Cartilage Transfer/osteochondral autograft transfer- In osteochondral grafting we move cartilage and bone (osteochondral autograft) from non weight bearing areas of the same knee joint and replace it cartilage to the area of damage.it can be done both open and arthroscopically.
- Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI)- ACI is a procedure that grows cartilage cells in a lab, and then inserts the newly grown cartilage into the area of damage.
Dr.anil sharma do both surgical and nonsurgical treatment of OCD. He mostly do all these procedure arthroscopically. So you recover early and there is very less chance of arthrofibrosis.